Prototype Models: Elevating Architectural Designs
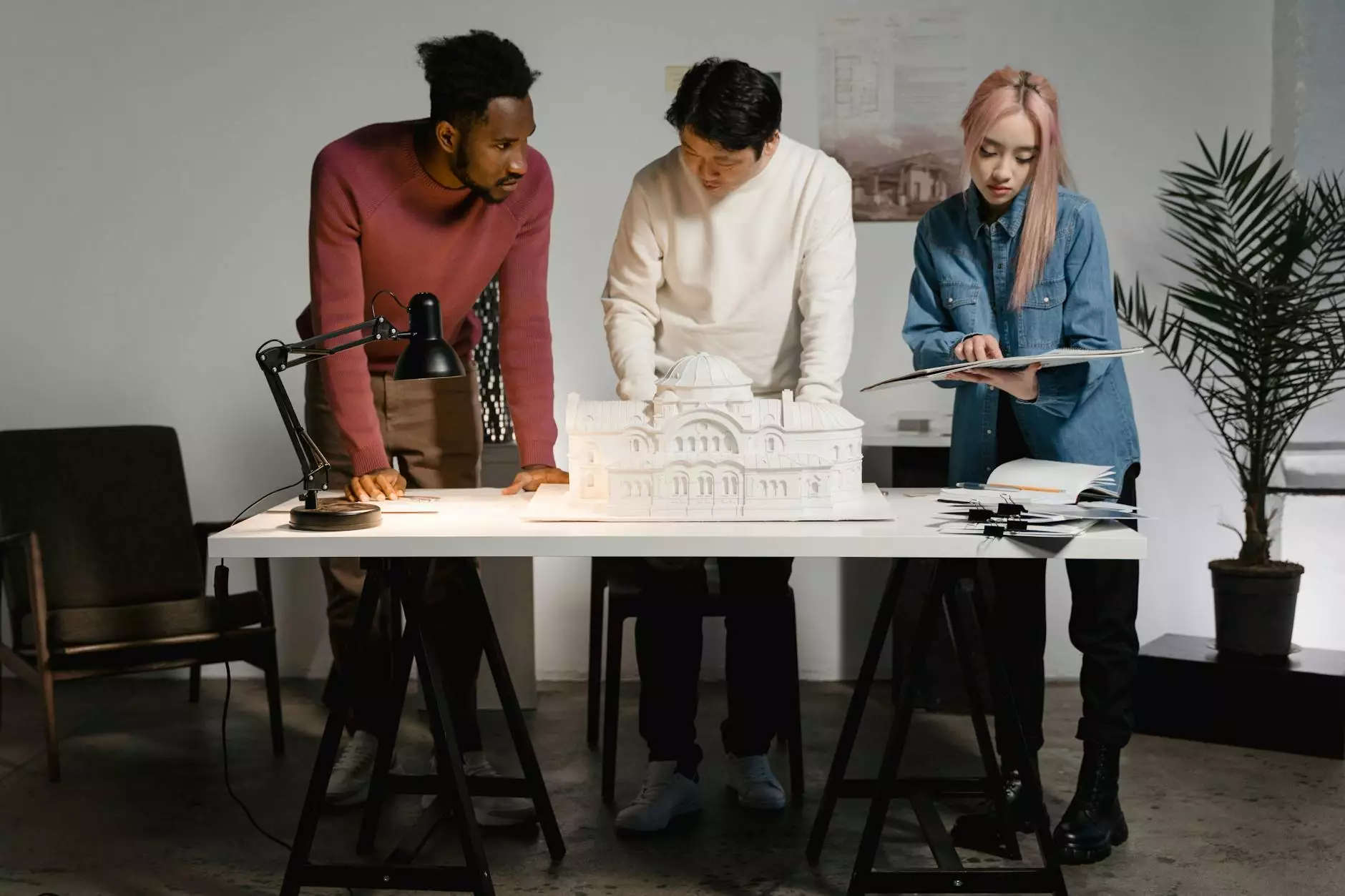

In the field of architecture, effective communication and visualization are paramount. Prototype models serve as a bridge between ideas and reality, offering a tangible representation of architectural concepts. This article delves into the significance of prototype models in the architecture industry, focusing on their benefits, applications, and how they can enhance your business when used effectively.
The Significance of Prototype Models in Architecture
Prototype models are not just physical representations of design concepts; they are essential tools that architects employ to articulate their visions. By creating detailed and accurate models, architects can:
- Visualize Concepts: Prototype models allow architects to see their designs in three dimensions, providing a clearer understanding of proportions, spatial relationships, and aesthetic qualities.
- Facilitate Communication: Models act as a universal language, enabling architects to convey complex ideas to clients, stakeholders, and construction teams effectively.
- Simplify Problem-Solving: By observing a model, architects can identify potential design flaws and challenges early in the process, thus avoiding costly alterations later on.
- Enhance Marketing Efforts: High-quality models can be powerful marketing tools, helping to attract clients by vividly illustrating the architect's vision.
Understanding Different Types of Prototype Models
There are various types of prototype models that can be employed throughout the design and construction processes. Each type serves specific purposes and can be tailored to meet the needs of different stakeholders:
1. Conceptual Models
Conceptual models are often the first representation of an idea. These models provide a basic visual framework of the proposed structure and are fundamental during the initial brainstorming sessions. They are typically quick and inexpensive to produce, focusing more on shape and mass rather than intricate details.
2. Presentation Models
Presentation models are designed for stakeholders and clients, showcasing the architecture's aesthetics and design intent. These models are more detailed and are usually crafted with high materials to ensure they convey the visual qualities of the final project. Suitable for presentations, these models can evoke emotional responses and effectively communicate the designer's vision.
3. Working Models
These models, also known as functional models, are built to assess the feasibility of a design. They might include moving parts or comprise actual building materials to test specific functions, such as light entry and airflow. Working models are essential for refining designs based on physical interactions.
4. Scale Models
Scale models are accurate representations of the final structure but reduced in size. They serve various purposes, from client presentations to urban studies, helping visualize how a new structure will fit into its environment. Scale models also provide insights into how a building functions within its context.
5. Digital Models
With advancements in technology, digital models have become an integral part of architectural design. They are created using software tools and can simulate lighting, texture, and even virtual tours. Digital modeling allows for instant revisions and experimentation, streamlining the design process.
The Process of Creating Prototype Models
The creation of prototype models can be broken down into several key phases, each integral to developing a successful representation of an architectural idea.
1. Initial Design and Sketching
The first stage in creating a prototype model is the conceptualization of ideas. Architects typically begin with sketches that outline the basic form and function of a proposed design. This phase is crucial for setting the foundation and direction for the model.
2. Modeling Materials Selection
Choosing the right materials is vital for the model's purpose and durability. Options vary from cardboard and foam board for quick models to high-quality woods and plastics for presentation models.
3. Assembling the Model
During this phase, builders assemble the model according to the design specifications. Advanced techniques may involve laser cutting, 3D printing, or handcrafting. Attention to detail during this phase is critical, as it affects the model's effectiveness and clarity.
4. Evaluation and Feedback
Once the prototype model is assembled, it should be evaluated by peers, clients, and stakeholders. Feedback is invaluable in determining whether the model effectively communicates the intended design, allows for the identification of areas for improvement, and suggests modifications if necessary.
Benefits of Using Prototype Models in Architecture
Implementing prototype models into architectural projects offers numerous advantages, which in turn can contribute to a more successful business outcome:
1. Improved Client Understanding
Clients often struggle to visualize designs from blueprints or 2D sketches alone. Prototype models provide a tactile experience, allowing clients to understand the dimensions, materials, and aesthetics of a project more intimately.
2. Enhanced Collaboration
The architectural process involves multiple stakeholders, including engineers, contractors, and developers. Models foster collaborative discussions by providing a concrete basis for conversations, ensuring everyone is aligned on the design intentions.
3. Reduced Change Orders
By identifying design flaws early through model review, architects can reduce the number of change orders that may arise during construction. Fewer changes lead to more on-time project deliveries and can significantly enhance profitability.
4. Boosted Efficiency
Prototype models allow for fast iterations and modifications. The ability to test different designs quickly can streamline the architectural process and lead to better end results.
Case Studies: Success Stories with Prototype Models
Case Study 1: Modern Skyscraper Development
An architectural firm was tasked with designing a new skyscraper in a dense urban area. They decided to create a series of presentation models that included the building's scale model alongside surrounding structures and landscapes.
This approach enabled the firm to demonstrate the skyscraper's impact on the skyline and urban flow, ultimately winning approval from city planners and local stakeholders. The visual representation facilitated productive discussions and showcased their commitment to harmonizing with the existing architecture.
Case Study 2: Community Park Planning
In another instance, a firm utilized a working model to plan a community park. They built a functional prototype to simulate foot traffic and recreational areas. During community meetings, attendees could physically interact with the model, providing instant feedback about preferred features and functionalities.
This collaborative approach not only ensured that the design met the community's needs but also built trust and excitement among residents as they could see their ideas represented in the final concept.
Best Practices for Implementing Prototype Models
To maximize the benefits of prototype models, architects and firms should consider the following best practices:
- Incorporate Feedback Early: Engage clients and stakeholders in the early stages of modeling to ensure their insights and preferences shape the design.
- Invest in Quality Materials: Depending on the purpose of the model, using high-quality materials can enhance realism and engage viewers more effectively.
- Utilize Technology: Leverage digital modeling tools to complement physical prototypes, offering versatility and detailed visualizations.
- Train Team Members: Ensure that all team members are skilled in both traditional modeling techniques and modern digital tools, fostering a versatile, adaptive team.
Conclusion: The Future of Prototype Models in Architecture
As the architectural landscape evolves, the importance of prototype models remains steadfast. They serve not only as a means of visual representation but also as critical tools for collaboration, problem-solving, and client engagement. By embracing the power of prototype models, architects can enhance their design processes, improve stakeholder communication, and ultimately deliver exceptional results.
As you consider the integration of prototype models into your architectural practice, remember that these tools can be a game-changer. They provide a distinct competitive edge in a crowded market, elevate client relationships, and pave the way for innovative architectural solutions. Begin harnessing the potential of prototype models today, and watch your architectural business reach new heights.